Notes
Goal: Understand HTML’s full name, history, and purpose. It’s the foundation—sites can exist with just HTML (early web did).
Key Concepts
- HTML = HyperText Markup Language
- HyperText: Text that links to other documents (hyperlinks—blue underlined text that jumps to another page).
- Markup Language: Uses tags to “mark up” content (tell browser how to structure/display it), like editors mark manuscripts for bold/underline.


- History:
- First websites = pure HTML.
- Invented by Tim Berners-Lee (also WWW/Internet pioneer).
- World’s first site: Full of hyperlinks linking HTML files.

- Role: Defines content & structure (browser renders HTML alone into a basic site).
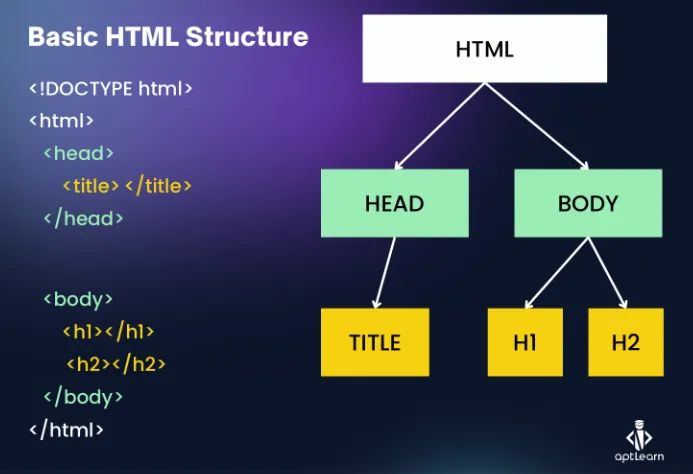
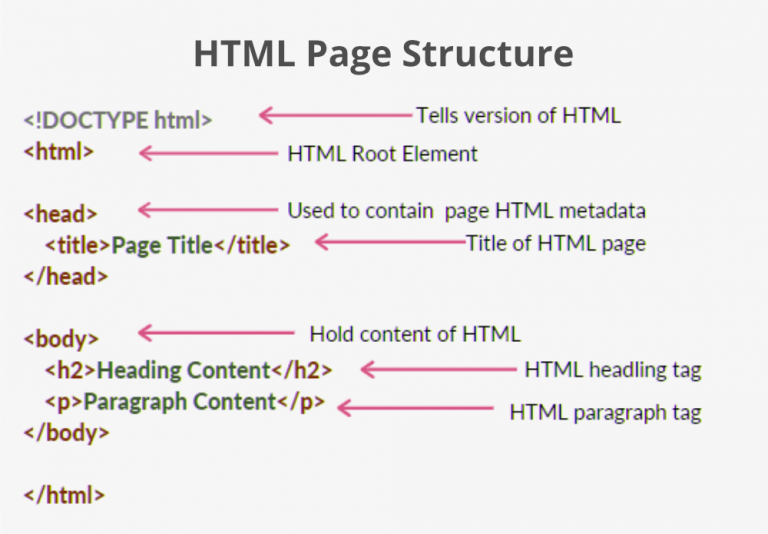
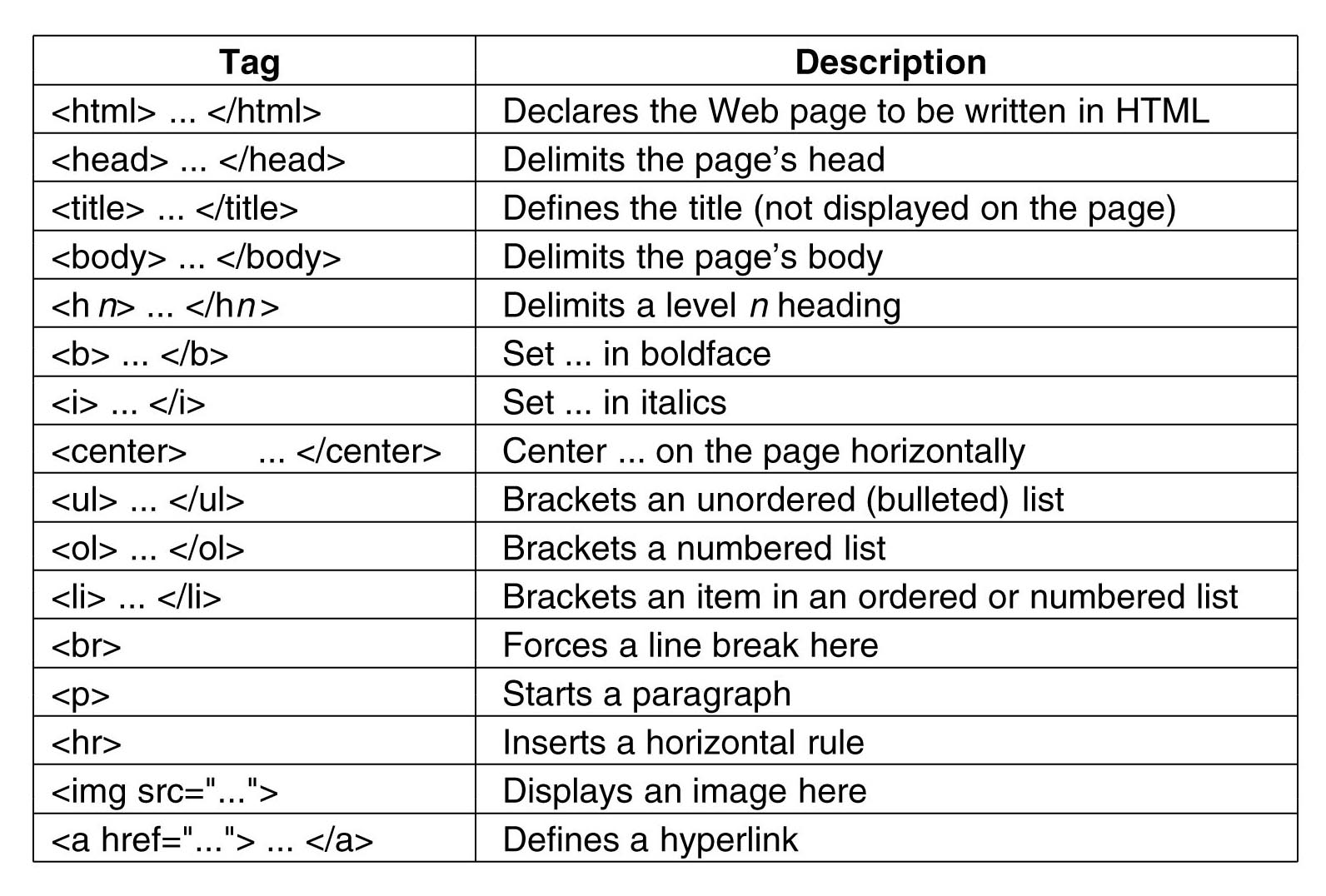
- Tags: Hundreds exist, but focus on essentials (e.g., headings
<h1>-<h6>, paragraphs<p>). Course covers as needed—no memorizing all!
Connections to Other Topics
- Builds on “How Websites Work” (HTML = first file browser loads).
- Hyperlinks → Later: Anchor tag
<a>. - Next: Heading tags (one of the oldest).
To Review / Resources
- Visit first website: info.cern.ch (try clicking links!).
- No need to learn all tags now—learn by doing.
Summary: HTML is HyperText (clickable links) Markup Language (tags for structure). Powers basic sites alone; foundation of the web since Tim Berners-Lee.